Discovery & Approval
DRUG

In the previous section, drug discovery, the lead compound is identified and it will now subjects to drug development process. The first development process involves pre-clinical trial studies, mostly pharmacological studies. The purpose of pharmacological studies is to determine the safety and effectiveness of the lead compound to yeild a potential drug for clinical trial. Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetics and toxicity are the key to concern in pharmacology. (Ng.R, 2003)
Pharmacodynamic - the actions of the drug on the target
Pharmacokinetics - actions of the body on the drug
Toxicity - determine the safety of the potential drug

-
At pre-clinical tial steps, drug molecules decrease to 250 compounds
-
Spending about 533 millions
-
Only 5 % chance for approving the drug onto the market.
-
Need about 3-6 years
Remember this?


Pre-Clinical Studies
Pharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamic is the relationship between drug at the site of action and drug effects. Drugs need to bind to their specific target sites/receptor to elicit a response.
D + R D*R Response
(where D is the drug, R is the receptor, and D*R is drug receptor complex.)
Scientists are responsible to find out the effect of the drug
on particular response. For instance, heart rate, enzyme levels,
muscle relaxation and contration and etc. Another way of
saying, the study of pharmacodynamics is used to determine
dose-response effect. (Ng.R, 2003)
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics is the study of the kinetics of AMDE (absorption, metabolism, distribution and elimination) of drugs. It analyses how what the drug does to the body after being administed, including transportation of the drug to the side of action to elicit its response. Figure >> summaries PKPD study.

Therefore, the data obtained from PKPD allow to set the dose and dosing regimen for the clinical trials.
In Vitro/ Vivo Analysis
In vitro analysis is a good starting point to evaluate pharmacological response. This is carried out in the test tube.
In vivo analysis is conducted in animals to study the drug effect on living organisms. Mice and rats are preffered to used as an animal studies, others such as guinea pigs, rabbit, hamsters are also been used.
The study using animals are regulated under GLP (Good Laboratory Pratice)
In Vitro / In Vivo Correlations
FDA defined in vitro / in vivo correlation (IVIVC) as "a predictive mathematical model describing the relationship between an in-vitro property of a dosage form and an in-vivo response". In other word, IVIVC is highly useful to predict in vivo properties based on the results from in vitro experiments. In traditional sense, IVIC is applied to pharmaceutical formulation and the results closely related to bioavailability/bioequivalence studies. (Landersdorfer. C, 2015)
BCS Biopharmacuetics Classification System
BCS classes I and III are highly soluble drugs. Hence, they are pplicable to be biowaivers. As highly soluble drug is reasonable to expect not causing any bioavailibility problems, serving as similar dissolution profiles and the bioequivalence study may be waived. (Landersdorfer. C, 2015)
Bioavailability - The rate and extent to which the active ingredient is absorbed from a drug product and becomes available at the site of
action. (Medumaze)
Bioequivalence - is the absence of a significant difference in the rate and extent to which the active ingredient is absorbed from a drug product and becomes available at the site of action when two "presumed identical" products are administered at the same molar dose under similar conditions in an appropriately design study. (Medumaze)

Formulation
API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) must be formulated with excipients into final form that suitable to be administered to the patients. The most common dosage form are caspules and tablets which administered orally. This delivery method provides certain convenience for pateints. (Ng.R, 2003)
The purpose of adding excipients in the formulation : (Ng.R, 2003)
> Control the release of drug substance in the body
> Improve the assimilation process and bioavailability
> Enhance drug dissolution as disintegration promoters
> Extend the stability and shelf life of the drug as antioxidants or preservatives
> Aid in the manufacturing processes in the form of fillers, lubricants, wetting agents and solubilizers
> Mask an unpleasant taste of the active pharmaceutical ingredient
> Use as an aid for identification of the product
Exicipients - any component, other than active substance(s),
intentionally added to the formulation of a dosage
form. (US Pharmacopeia)
Example of the drug formulation:
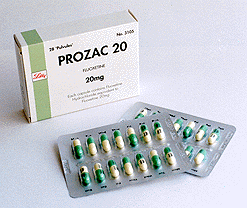
Prozac
An antidepressant in 10, 20 and 40 mg doses.
Active ingredient: fluoxethine hydrochloride
Excipients: starch, gelatin, silicone, titanium dioxide, iron oxide etc.
The common excipients used for tablets/ capsules are classified into different classes summarized in table below.
The brief functions of excipients are listed below: (Hill, R., & Rang, H. P, 2013)
Filler -> produce manageable size tablet (generally 50-500 mg)
Disintegrant -> ensures the tablet disintegrates rapidly in the gastrointestinal tract
Binder -> assists compaction into a solid tablet that will not crumble
Glidants -> improve powder flowability
Lubricants -> prevent ingredient from clumbing together and from sticking to the tablet punches.
Antiadherent -> reduce the adhesion between powders and punches faces.
When excipients are added into the formulation of the drug substances/API. Manufacturing of new drugs are regulated under GMP (Good Manufacturing pratices).

Intellectual Property
Patent is not the only form of intellectual property. However, it is the most improtant for pharmaceutical industry to protect their investment.
According to FDA, a patent is "a property right issued by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) to an inventor to exclude others from making, using, offering for sale, or selling the invention throughout the United States or importing the invention into the United States” for a limited time, in exchange for public disclosure of the invention when the patent is granted".
Generally, a new patent is usually last for 20 years from the date on which the application for the patent is filed in the United States.
The invention must: (Morton.D, 2015)
-
be new (have novelty)
-
have an inventive step that is not obvious to someone with knowledge and experience in the subject
-
be capable of being made or used in some kind of industry
Patent is VERY important especially for pharmaceutical industry as once the chemical structure of the drug is published, others can simply copy the idea and design, they do not spend much money on R&D, and sell the product cheeply and still make their profit.
Eli Lilly, the maker of Prozac, the world top selling antidepressant drug, prescribed to more than 54 million people worldwilde. It was approved by FDA in 1987. Once the Eli Lilly's Prozac patent protection was expired, Barr laboratories stepped in and took over the generic version of Prozac in August 2001. As a result, 29% of the value of Eli Lilly stock was lost in 1 day - over $35 billion. This is a SERIAL MONEY LOST. (Hill, R & Rang, H.P ,2013)


Reference
1. Ng, R. (2003) Drug Development and Preclinical Studies, in Drugs: From Discovery to Approval, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA. doi: 10.1002/0471722804.ch5
2. Hill, R., & Rang, H. P. (2013). Drug discovery and development : Technology in transition (2nd ed.). Edinburgh ; New York: Elsevi
3. Landersdorfer. C (2015), "4 Target effects V06 2015 File ", retrieved from http://moodle.vle.monash.edu/pluginfile.php/3454952/mod_resource/content/0/4_Target_effects_V06_2015.pdf
4. Landersdorfer. C (2015), "1 In Vitro In Vivo Correlations Lecture slide File", retrieved from http://moodle.vle.monash.edu/pluginfile.php/3147507/mod_resource/content/1/1_In_Vitro_In_Vivo_Correlations_V03_4on1.pdf
5. MeduMaze. Supplemental Information and Alphabetical Glossary of Terms, Drug Development & Approval Game
6. Siddiqui, M. R., et al.(2013) "Analytical techniques in pharmaceutical analysis: A review." Arabian Journal of Chemistry. Available online 23 April 2013, ISSN 1878-5352, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.04.016.
7. Ohannesian, L., & Streeter, Anthony J. (2002). Handbook of pharmaceutical analysis (Drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences ; v. 117). New York: Marcel Dekker.
8. Morton.D (2015), ''patents 2015-update", retrieved from http://moodle.vle.monash.edu/pluginfile.php/3521645/mod_resource/content/0/patents%202015%20Update.pdf
( Landersdorfer. C, 2015)
( Landersdorfer. C, 2015)
Pharmaceutical Analysis
It is a quantitative measurement of the API and related compounds in the pharmaceutical products. The primary goal of pharmaceutical analysis is to assure the quality of the drug. The quantitative measurement includes determining the identity, purity, content, stability of starting material, API and excipients. In addtion, these determinations need to be
BECAUSE,
the data is used for manufacturing control, stability evaluation, and shelf life-prediction.
There are several analytical techniques commonly employed by pharmacutical analytical chemist can do the quantitative measurement. This includes ultraviolet/visible spectroscopy, infrared spectrophotometry, atomic spectrophotometry, molecular emission spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance spectrocopy, mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, high-performannce liquid chromatography and etc.
Below illustrates the principle behind of some analytical instruments.
After the drug substances/ API has been formulated into the dosage form with the present of excipients. Is the identity of the drug correct in the formulation? Does the formulation contain additional impurities? How stable is the drug in the formulation? Do the identity of purity of the excipients meet the specification?
Accuracy
Precision
Reliability
Siddiqui, M. R., et al.(2013)


